Toyota Camry (XV70): System Description
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
NAVIGATION SYSTEM OUTLINE
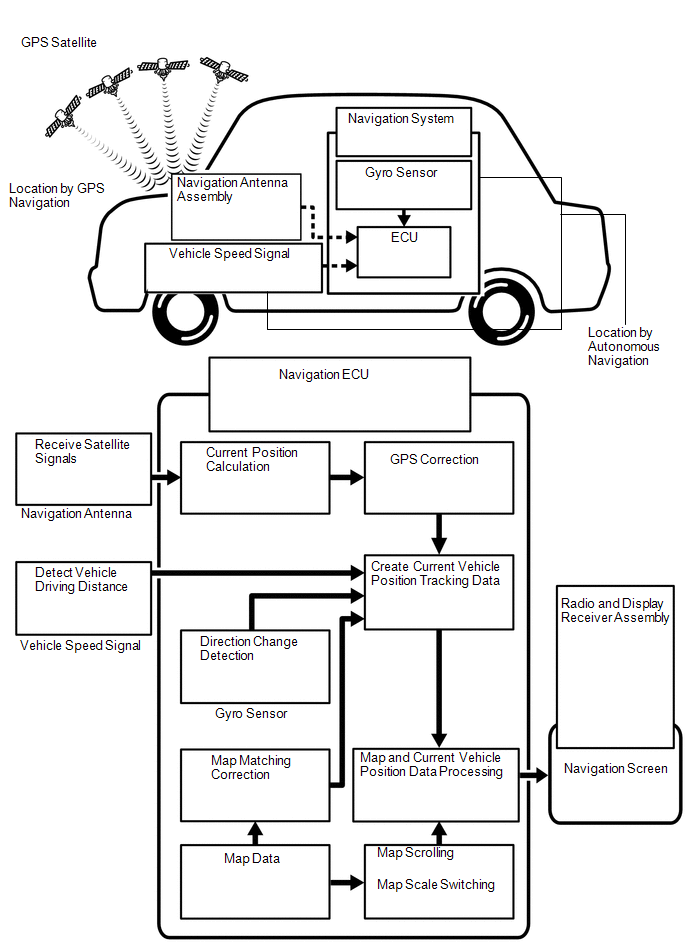
(a) Vehicle position tracking methods
It is essential that the navigation system correctly tracks the current vehicle position and displays it on the map. There are 2 methods to track the current vehicle position: autonomous (dead reckoning) and GPS* (satellite) navigation. Both navigation methods are used in conjunction with each other.
*: GPS (Global Positioning System)
|
Operation | Description |
|---|---|
|
Vehicle Position Calculation | The navigation ECU calculates the current vehicle position (direction and current position) using the direction deviation signal from the gyro sensor and driving distance signal from the vehicle speed sensor and creates the driving route. |
|
Map Display Processing | The navigation ECU processes the vehicle position data, vehicle driving track and map data from the internal memory. |
|
Map Matching | The map data from the internal memory is compared to the vehicle position and driving track data. Then, the vehicle position is matched with the nearest road. |
|
GPS Correction | The vehicle position is matched to the position measured by the GPS. Then, the GPS measurement position data is compared with the vehicle position and driving track data. If the position is very different, the GPS measurement position is used. |
|
Distance Correction | The vehicle speed signal includes the error caused by tire wear and slippage between the tires and road surface. Distance correction is performed to account for this. The navigation ECU automatically offsets the signal to make up for the difference between it and the distance data of the map. The offset is automatically updated. |
HINT:
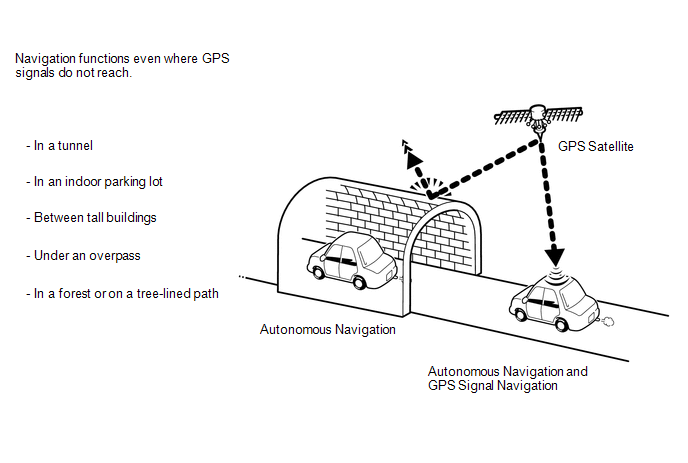
The combination of autonomous and GPS navigation makes it possible to display the vehicle position even when the vehicle is in places where GPS signals cannot be received. When only autonomous navigation is used, however, the mapping accuracy may slightly decrease.
(b) Autonomous navigation
This method determines the relative vehicle position based on the driving track determined by the gyro sensor located in the navigation ECU and the vehicle speed signal.
(1) Gyro sensor
Used to calculate the direction by detecting angular velocity. It is located in the navigation ECU.
(2) Vehicle speed signal
Used to calculate the vehicle driving distance.
(c) GPS* navigation (Satellite navigation)
This method detects the absolute vehicle position using radio waves from GPS satellites.
*: GPS satellites were launched by the U.S. Department of Defense for military purposes.
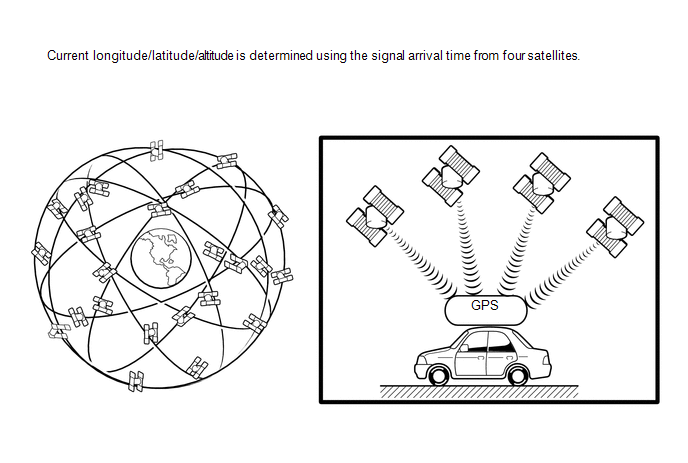
|
Number of Satellites | Measurement |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2 or less |
Measurement is impossible | Vehicle position cannot be obtained because the number of satellites is not enough. |
|
3 | 2-dimensional measurement is possible |
Vehicle position is obtained based on the current longitude and latitude. (This is less precise than 3-dimensional measurement.) |
|
4 | 3-dimensional measurement is possible |
Vehicle position is obtained based on the current longitude, latitude and altitude. |
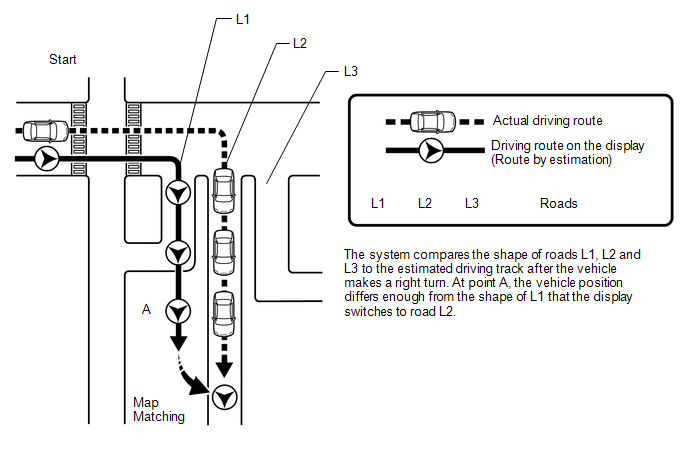
(d) Map matching
The current driving route is calculated by autonomous navigation (according to the gyro sensor and vehicle speed signal) and GPS navigation. This information is then compared with possible road shapes from the map data in the internal memory and the vehicle position is set onto the most appropriate road.
USB AUDIO SYSTEM FUNCTION OUTLINE
(a) The No. 1 stereo jack adapter assembly is equipped with a USB connector. Connecting a USB device or "iPod" to the No. 1 stereo jack adapter assembly allows music files to be played. Not only is it possible to play music from a USB device with audio functions, it is also possible to play MP3, WMA, AAC, WAV (LPCM), FLAC, ALAC or OGG Vorbis music files that are stored on a USB device. In addition, "iPod" control software is installed, allowing file selection from playlists and operation using shuffle mode.
HINT:
Operation through the controls of a USB device or "iPod" cannot be performed while it is connected.
(b) USB audio system compatible devices
(1) USB device
The following device formats can be used:
|
Compatible USB device formats |
|
MP3, WMA, AAC, WAV (LPCM), FLAC, ALAC and OGG Vorbis files written to a USB device with any format other than those listed above may not be played correctly, and their names and folder names may not be displayed correctly.
Items related to standards and limitations are as follows:
- Maximum directory hierarchy: 8 levels
- Maximum number of folders in device: 3000 (including the root folder)
- Maximum number of files in device: 9999
- Maximum number of files per folder: 255
(2) "iPod"
"iPhone", "iPod", "iPod nano" and "iPod touch" are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries.
The following "iPod nano", "iPod touch" and "iPhone" devices can be used with this system.
- "iPhone X"
- "iPhone 8 Plus"
- "iPhone 8"
- "iPhone 7 Plus"
- "iPhone 7"
- "iPhone SE"
- "iPhone 6s Plus"
- "iPhone 6s"
- "iPhone 6 Plus"
- "iPhone 6"
- "iPhone 5s"
- "iPhone 5c"
- "iPhone 5"
- "iPhone 4s"
- "iPod touch" (6th generation)
- "iPod touch" (5th generation)
- "iPod nano" (7th generation)
HINT:
- Depending on differences between models or software versions etc., some models might be incompatible with this system.
USB VIDEO SYSTEM FUNCTION OUTLINE
(a) Playable video file standards
|
File format | MPEG-4, AVI Container, Windows Media Video |
|
Corresponding screen size | MAX 1920 x 1080 |
|
Corresponding frame rate |
MAX 60i/30p |
HIGH-RESOLUTION SOUND SOURCE OUTLINE
(a) This device supports high-resolution sound sources.
(b) The definition of high-resolution is based on the standards of groups such as the CTA (Consumer Technology Association).
(c) The following formats and media can be used:
|
Supported formats | WAV (LPCM), FLAC, ALAC, OGG Vorbis |
|
Playable media | USB |
FILE INFORMATION OUTLINE
(a) Playable MP3 file standards
|
Compatible standard | MPEG1 LAYER3, MPEG2 LSF LAYER3 |
|
Compatible sampling frequency |
|
| Compatible bit rate |
|
| Compatible channel mode |
Stereo, joint stereo, dual channel, monaural |
(b) Playable WMA file standards
|
Compatible standard | WMA Ver. 7, 8, and 9 |
|
Compatible sampling frequency |
32, 44.1, 48 (kHz) |
|
Compatible bit rate (Only compatible with 2-channel playback) |
|
(c) Playable AAC file standards
|
Compatible standard | MPEG4/AAC-LC |
|
Compatible sampling frequency |
11.025, 12, 16, 22.05, 24, 32, 44.1, 48 (kHz) |
|
Compatible bit rate |
|
(d) Playable WAV (LPCM) file standards*
| *: Files with a sample rate higher than 48kHz are down-converted to 48kHz/24bit. | |
| Compatible sampling frequency |
8/11.025/12/16/22.05/24/32/44.1/48/88.2/96/176.4/192 (kHz) |
|
Compatible bit rate | 16/24 (bit) |
(e) Playable FLAC file standards*
| *: Files with a sample rate higher than 48kHz are down-converted to 48kHz/24bit. | |
| Compatible sampling frequency |
8/11.025/12/16/22.05/24/32/44.1/48/88.2/96/176.4/192 (kHz) |
|
Compatible bit rate | 16/24 (bit) |
(f) Playable ALAC file standards*
| *: Files with a sample rate higher than 48kHz are down-converted to 48kHz/24bit. | |
| Compatible sampling frequency |
8/11.025/12/16/22.05/24/32/44.1/48/64/88.2/96 (kHz) |
|
Compatible bit rate | 16/24 (bit) |
(g) Playable OGG Vorbis file standards*
| *: Files with a sample rate higher than 48kHz are down-converted to 48kHz/24bit. | |
| Compatible sampling frequency |
8/11.025/16/22.05/32/44.1/48 (kHz) |
|
Compatible bit rate |
|
(h) ID3 tag, WMA tag, AAC tag, TAG and Vorbis comment
(1) Additional text information called an ID3 tag can be input to MP3 files. Information such as song titles and artist names can be stored.
HINT:
This player is compatible with ID3 tags of ID3 Ver. 1.0 and 1.1, and ID3 Ver. 2.2 and 2.3. (Number of characters complies with ID3 Ver. 1.0 and 1.1, and ID3 Ver. 2.2 and 2.3.)
(2) Additional text information called a WMA tag can be input to WMA files. Information such as song titles and artist names can be stored.
(3) Additional text information called an AAC tag can be input to AAC files. Information such as song titles and artist names can be stored.
(4) Additional text information called a TAG can be input to WAV (LPCM), FLAC, ALAC files. Information such as song titles and artist names can be stored.
(5) Additional text information called a Vorbis comment can be input to OGG Vorbis files. Information such as song titles and artist names can be stored.
(i) Usable media
(1) Only USB devices can be used to play WAV (LPCM)/FLAC/ALAC/OGG Vorbis files.
(j) Usable media format
(1) Standards and restrictions
|
Maximum directory levels | 8 levels |
|
Maximum number of characters for a folder name/file name |
32 characters |
| Maximum number of folders |
192 (Including empty folders, root folders, and folders that do not contain MP3/WMA/AAC files) |
|
Maximum number of files in a disc | 255 (Including non-MP3/WMA/AAC files) |
(k) File names
(1) Only files with an extension of ".mp3", ".wma", ".m4a", ".wav", ".flac", ".alac", ".ogg" and ".oga" can be recognized and played as MP3, WMA, AAC, WAV (LPCM), FLAC, ALAC or OGG Vorbis files.
(2) Save MP3, WMA, AAC, WAV (LPCM), FLAC, ALAC or OGG Vorbis files with an extension of ".mp3", ".wma", ".m4a", ".wav", ".flac", ".alac", ".ogg" or ".oga".
NOTICE:
If non-MP3, non-WMA, non-AAC, non-WAV (LPCM), non-FLAC, non-ALAC or non-OGG Vorbis files are saved with an extension of ".mp3", ".wma", ".m4a", ".wav", ".flac", ".alac", ".ogg" or ".oga", those files may be wrongly recognized as MP3, WMA, AAC, WAV (LPCM), FLAC, ALAC or OGG Vorbis files and played. A loud noise may occur and damage to the speakers may result.
"Bluetooth" OUTLINE
.png)
|
*1 | Radio and Display Receiver Assembly (Built-in "Bluetooth" Antenna) |
- | - |
|
*a | Example |
*b | Cellular Network |
|
*c | Cellular Phone ("Bluetooth" Compatible Type) |
*d | Portable Audio Player ("Bluetooth" Compatible Type) |
|
*e | "Bluetooth" Wireless Connection |
- | - |
(a) "Bluetooth" is a trademark owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc.
(b) "Bluetooth" is a wireless connection technology that uses the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
HINT:
The communication performance of "Bluetooth" may vary depending on obstructions or radio wave conditions between communication devices, electromagnetic radiation, communication device sensitivity or antenna capacity.
(c) Hands-free function
(1) The "Bluetooth" built-in radio and display receiver assembly and a "Bluetooth" compatible cellular phone* can be connected using a "Bluetooth" wireless connection. This enables the use of the hands-free function on the cellular phone even if the phone is in a pocket or bag. For this reason, it is not necessary to use a connector or cable to connect the cellular phone.
*: Some versions of "Bluetooth" compatible cellular phones may not function properly.
(2) The hands-free function uses a "Bluetooth" wireless connection. A "Bluetooth" wireless connection can be affected by uncertain elements, such as vehicle location, time of day, etc. Therefore, problems related to establishing connection may be caused temporarily by "Bluetooth" connection conditions. It is necessary to check the frequency of occurrence, connection conditions using another cellular phone, etc. when performing diagnosis.
(3) Compatible hands-free devices
|
Required "Bluetooth" specifications | Ver. 2.0 or higher (Ver. 4.2 recommended) |
|
Compatible profiles |
|
| Maximum number of hands-free devices that can be registered (including audio devices) |
5 |
- *1: This profile is necessary when using the hands-free function.
- *2: This profile is necessary when transferring the phonebook data.
- *3: This profile is necessary when using the toyota entune function.
- *4: This profile is necessary when using the message function (w/ SMS/MMS/e-mail Function).
HINT:
- "Bluetooth" compatible cellular phone can be checked at http://www.toyota.com/entune/.
- The amount of remaining battery charge displayed on the radio and display receiver assembly may be different from that of the "Bluetooth" device.
(d) "Bluetooth" audio function
(1) The "Bluetooth" built-in radio and display receiver assembly and a "Bluetooth" compatible portable audio player* can be connected using a "Bluetooth" wireless connection. This enables files stored in the portable audio player to be heard from the vehicle speakers. In addition, operations such as play/stop can be performed directly from the radio and display receiver assembly.
*: Some versions of "Bluetooth" compatible audio players may not be able to be connected via the "Bluetooth" function, or music may play, but functions available using the radio and display receiver assembly may be limited.
(2) Compatible "Bluetooth" audio devices
|
Required "Bluetooth" specifications | Ver. 2.0 or higher (Ver. 4.2 recommended) |
|
Compatible profiles |
|
| Maximum number of audio devices that can be registered (including hands-free devices) |
5 |
RADIO DESCRIPTION
(a) Radio frequency band
(1) Radio broadcasts use the radio frequency bands shown in the table below.
.png)
(b) Service area
(1) The service areas of AM and FM broadcasts are vastly different. Sometimes an AM broadcast can be received very clearly but an FM stereo broadcast cannot. FM stereo has the smallest service area, and is prone to pick up static and other types of interference such as noise.
.png)
|
*a | FM (Stereo) |
|
*b | FM (Monaural) |
|
*c | AM |
(c) Radio reception problems
HINT:
In addition to static, other problems such as "phasing", "multipath" and "fade out" exist. These problems are not caused by electrical noise, but by the radio signal propagation method itself.
(1) Phasing
AM broadcasts are susceptible to electrical interference and another kind of interference called phasing. Occurring only at night, phasing is the interference created when a vehicle receives 2 radio wave signals from the same transmitter. One signal is reflected off the ionosphere and the other signal is received directly from the transmitter.
.png)
|
*a | Phasing |
|
*b | Ionosphere |
(2) Multipath
Multipath is a type of interference created when a vehicle receives 2 radio wave signals from the same transmitter. One signal is reflected off buildings or mountains and the other signal is received directly from the transmitter.
.png)
|
*a | Multipath |
(3) Fade out
Fade out is caused by objects (buildings, mountains and other large obstructions) that deflect part of a signal, resulting in a weaker signal when the object is between the transmitter and vehicle. High frequency radio waves, such as FM broadcasts, are easily deflected by obstructions. Low frequency radio waves, such as AM broadcasts, are less likely to be deflected.
.png)
|
*a | Fade Out |
(d) Noise problem
Technicians must have a clear understanding about each customer's noise complaint. Use the following table to diagnose noise problems.
|
Radio Frequency | Noise Occurrence Condition |
Presumable Cause |
|---|---|---|
|
AM | Noise occurs in a specific area |
Foreign noise |
| Noise occurs when listening to an intermittent broadcast |
An identical program transmitted from multiple towers can cause noise where the signals overlap | |
|
Noise occurs only at night | Signal phasing | |
|
FM | Noise occurs while driving in a specific area |
Multipath resulting from a change in FM frequency |
"HD Radio" FUNCTION OUTLINE (w/ HD Radio Function)
(a) The "HD Radio" system is a radio system that broadcasts in the IBOC (In-Band On-Channel) form that the iBiquity Co. has developed. By expanding the bandwidth per channel of conventional FM/AM bands, digital audio and data signals are additionally transmitted.
"HD Radio" technology is manufactured under license from iBiquity Digital Corporation. U.S. and Foreign Patents. "HD Radio" and the HD and HD Radio logos are proprietary trademarks of iBiquity Digital Corporation. Also, traffic and weather information can be received and displayed on the navigation screen.
SiriusXM FUNCTION OUTLINE (w/ SXM Function)
(a) SiriusXM (SXM) satellite radio is a satellite digital radio broadcast provided by SiriusXM Radio Inc. The broadcast (pay-type) is performed through satellites and terrestrial repeater networks. Several unique channels are available, and even if a vehicle changes locations, the same information can be received without breaks. Information such as song names, broadcast station names, etc. can be received.
NOTICE:
To receive pay-type broadcasts, the customer must enter into a pay-type contract with SiriusXM Satellite Radio Inc. After entering into a contract, registration of the Radio ID is necessary. Also, if parts are replaced, the Radio ID must be re-registered.
HINT:
When disconnecting the cable from the negative (-) battery terminal, the broadcast station logo data will be initialized. It takes a while for the broadcast station logo data to be updated to the latest data.
VEHICLE CUSTOMIZATION OUTLINE
(a) Customization of functions can also be performed on the multi-display screen. Refer to Owner's Manual for further information on customizable items for the navigation system.
HINT:
- Items available for customization via the navigation system can also be customized by using the Techstream.
- Some customize parameters displayed on the Techstream will be displayed on the vehicle customization screen for the navigation system. Users can customize these items.
AUTOMATIC SOUND LEVELIZER (ASL) FUNCTION OUTLINE
(a) The Automatic Sound Levelizer (ASL) function automatically adjusts the audio system volume in order to compensate for increased vehicle noise (vehicle noise tends to increase as vehicle speed increases). The ASL adjusts the volume based upon vehicle speed signals sent from the combination meter assembly.
DYNAMIC VOICE RECOGNITION FUNCTION OUTLINE (w/ Manual (SOS) Switch)
(a) There are two types of voice recognition; the voice recognition function uses voice recognition data stored in the onboard device. The other is communication based and uses voice recognition data sent from communication with the DCM (telematics transceiver) as audio signals to be stored at the center.
HINT:
Refer to the TOYOTA ENTUNE SYSTEM for information about communication based voice recognition.
Click here .gif)
MOBILE ASSISTANT FUNCTION OUTLINE (w/ Mobile Assistant Function)
(a) With a compatible portable device connected via "Bluetooth", this function allows the system to interface directly for voice recognition functions. The steering pad switch assembly is operated to start the Mobile Assistant function and the function is operated by using voice commands.
HINT:
Mobile assistant may not operate or the device may become unresponsive depending on the type of device connected, OS (iOS/Android) version or Google app version.
"Wi-Fi" hotspot OUTLINE (w/ "Wi-Fi" hotspot Function)
HINT:
- To use the "Wi-Fi" hotspot function, initial setup of the Toyota Entune App Suite function is necessary.
- To perform initial setup, refer to http://www.toyota.com/entune/.
(a) "Wi-Fi" is a worldwide wireless communication standard widely used as a short range communication tool.
(b) "Wi-Fi" is a trademark owned by Wi-Fi Alliance, a non-profit industry association.
(c) The radio and display receiver assembly uses the 2.4 GHz frequency band for "Wi-Fi" communication.
HINT:
The communication performance of "Wi-Fi" may vary depending on obstructions or radio wave conditions between communication devices, electromagnetic radiation, communication device sensitivity or antenna capacity.
"Apple CarPlay" FUNCTION OUTLINE (w/ "Apple CarPlay" Function)
(a) The "Apple CarPlay" function is a function that enables the head unit to operate applications on a smartphone by connecting the smartphone to the head unit using a dedicated cable.
HINT:
- Refer to the owner's manual included with the device for information about "Apple CarPlay" support.
- Some applications have a display restriction in consideration of safe driving.
"Android Auto" FUNCTION OUTLINE (w/ "Android Auto" Function)
(a) The "Android Auto" function is a function that enables the head unit to operate applications on a smartphone by connecting the smartphone to the head unit using a dedicated cable.
HINT:
- Refer to the owner's manual included with the device for information about "Android Auto" support.
- Some applications have a display restriction in consideration of safe driving.
COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
(a) Local Bus Communication Outline
.png)
|
*a | Example |
*b | Local Bus Communication Line |
|
*c | Master Unit |
*d | Slave Unit |
(1) Components of the navigation system communicate with each other via the local bus.
(2) The local bus uses a twisted pair of wires for its communication lines.
(3) The master unit of the local bus is the radio and display receiver assembly.
HINT:
- The radio and display receiver assembly has the resistance (108 to 132 Ω) necessary for communication.
- If a short or open occurs in the local bus circuit, communication is interrupted and the system will not operate normally.
(b) CAN Communication Outline
(1) The navigation system uses CAN communication between the radio and display receiver assembly and ECUs.
(c) AVC-LAN Outline
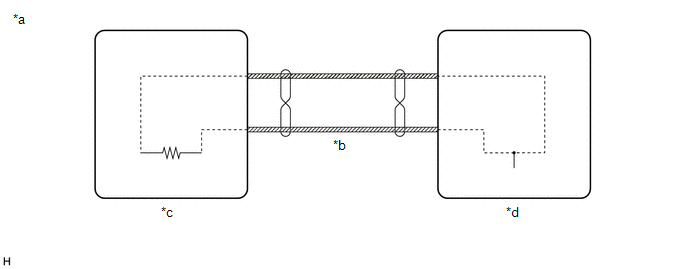
|
*a | Example |
*b | AVC-LAN Communication Line |
|
*c | Master Unit |
*d | Slave Unit |
(1) Components of the navigation system communicate with each other via AVC-LAN communication.
(2) The AVC-LAN uses a twisted pair of wires for its communication lines.
(3) The master unit of the AVC-LAN is the radio and display receiver assembly.
HINT:
- The radio and display receiver assembly has the resistance (60 to 80 Ω) necessary for communication.
- If a short or open occurs in the AVC-LAN circuit, communication is interrupted and the system will not operate normally.
DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTION OUTLINE
(a) The navigation system has a diagnostic function (the result is indicated on the master unit).

